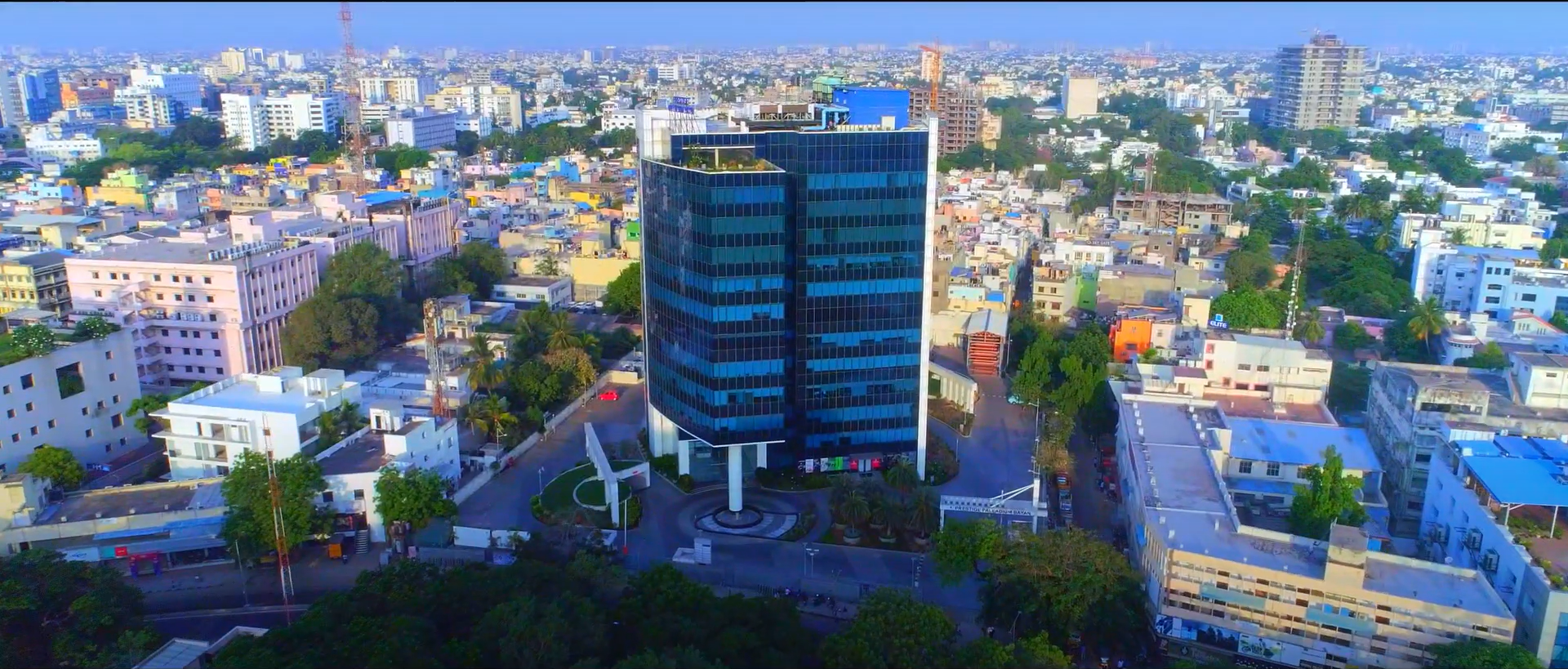
Every business leader today is facing one and the same tough reality that expensive, complex, and urgent is indeed the path for net-zero. The world needs trillions of investment. This is in order that climate commitments are met. Usual financing channels remain slow and limited. Often they also lack transparency. Because of this gap, companies, governments, as well as investors are being pushed to rethink just how climate finance is able to scale.
Here net-zero tokens then provide assistance. Businesses are able to access a more transparent, efficient, and globally accessible investment mechanism for turning real-world assets (RWAs) such as renewable energy projects, carbon credits, or else green bonds into blockchain-based tokens. It is not just all about the funding of climate projects; it is about building up trust, reducing down costs, and we must invite a broader participation into the ESG initiatives. For decision-makers, tokenization allows them to commercially align profitability with sustainability for tackling one of the greatest financial challenges of our time.
The Climate Finance Challenge for Net-Zero Targets
To reach net-zero emissions by 2050 as well as to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement is quite a task. Yearly, experts estimate the requirement to be $4.6 trillion, totaling an eye-watering $125 trillion in climate finance. These numbers underline a simple truth: the world risks falling short regarding its net-zero commitments if there are no scalable as well as accessible financing models.
Yet, right now the current tools for climate finance do age.
- Green bonds and loans: They are popular, but liquidity bottlenecks often tie up funds for long durations.
- Fragmented standards and reporting frameworks make actual impact hard to track also double-counting hard to prevent.
- High transaction costs: Customary intermediaries drive up costs since they discourage smaller investors also slow capital deployment.
The result? There are limits in participation, reporting that is opaque, and then capital flows are slow. This quite outdated system feels just like trying to actually run an infrastructure decades old on a modern type of economy for investors excited for meeting ESG goals and businesses. Net-zero tokenization has the promise to flip this model by making climate finance liquid and also transparent. It also makes climate finance accessible for both institutional and retail participants.
What Is Net-Zero Tokenization?
Net-zero tokenization mainly changes climate-focused real-world assets (RWAs) to digital tokens using a blockchain. Think about investing in renewable energy projects, using carbon credits, issuing green bonds, or cultivating sustainable farmland. Represented as tokens, these assets can be easily traded, tracked, and invested in place of being locked up in customary instruments.
This is a shift in the way that capital flows not simply just a technical upgrade for businesses. Enterprises with tokenized assets can attract investors across the globe, break down large projects, and build transparency into every stage of climate finance. The model opens the door for new participants. Before this, smaller investors as well as institutional giants had been unable to access high-value climate projects. Tokenization makes climate finance rather more democratic as well as scalable. Net-zero goals demand with precision this.
Key Technical Features of Net-Zero Tokenization
So from what does tokenized climate assets differ than how we finance? Technical features give this model a unique edge.
Liquidity and Fractional Ownership
Dividing tokenized assets into smaller units makes participation easier upon more investors. For instance, even a large solar farm can be broken down into fractional tokens now. This gives to even small-ticket investors access to the renewable energy markets. Tokenized assets can be traded 24/7 and create real liquidity unlike with green bonds that lock up capital for years.
Smart Contracts and Automated Compliance
Smart contracts automate much of the process and range from investment deals to compliance tests. For example, reporting can be built directly into the logic of the contract. Reporting follows worldwide ESG structures like ISSB or TCFD. Errors now are reduced and also delays are prevented. As well, administrative costs are able to be cut down.
Transparency and Traceability
Each tokenized transaction gets recorded on the blockchain providing an unchangeable activity record. This traceability level aids in greenwashing risk elimination, investor trust increases, and ESG audits gain ease plus reliability. Businesses can present impact metrics in real time instead of relying on fragmented reports months after the fact.
Global Accessibility
Tokenized assets can be accessible on a global scale, unlike customary markets that have geography or regulation-heavy intermediaries. Very quickly, a firm located in Asia can obtain funds from backers located in Africa or Europe. To annually reach trillions in climate finance, this is required. The nature of the borderless is vital for us.
Industry Use Cases of Net-Zero Tokenization
Tokenization is not just a buzzword, but industries now are already applying of it in climate finance. In an effort to support net-zero goals, different sectors are now leveraging tokenized real-world assets in this way:
Renewable Energy Scaling
Renewable energy projects often need billions initially. Consequently, access is limited to large institutions. Tokenization allows for those barriers to break down. Solar farms, wind projects, also hydroelectric initiatives can be fractionalized into tokens so that a wider range of investors can participate. A $500 million wind energy project, for example, can be tokenized into smaller, tradeable units. This tokenization enables businesses funds as well as even retail investors to contribute. Energy output tracking on-chain is ensured by IoT integration, linking investor returns directly to performance.
Carbon Credits and Emission Reduction Assets
Carbon markets have long faced issues like fragmented standards and double-counting. Tokenization holds actors accountable and ensures traceability. Businesses gain verifiable proof of ownership without tampering by converting carbon credits into tokens. Because of this, organizations can more easily meet compliance requirements. Also, more transparent ESG dashboards may be presented to some stakeholders. For example, emission reduction assets namely ERAs are tokenized on a blockchain can track every ton of CO₂, avoid it, ensure credibility, and then increase investor confidence.
Green Bonds for Sustainable Infrastructure
Liquidity is constrained because of the common design of green bonds, a vital tool of finance for climate projects. That can change tokenized green bonds. Issuing blockchain-based green bonds allows companies to offer investors fractional access with lower issuance costs along with easier trading. This model betters liquidity and betters transparency therefore investors can monitor real-time fund usage like sustainable transport systems, solar installation, or energy-efficient housing.
Sustainable Agriculture and Regenerative Practices
Global emissions are impacted in a large way by agriculture. Carbon sequestration also does have enormous potential within itself. Tokens help channel funds toward regenerative farming projects. For instance, farmlands are able to issue tokens related to their verified carbon storage. These farmlands do practice soil carbon capture. These tokens are purchased by investors supporting climate-positive practices thereby. Investors do also receive some measurable returns. For agricultural projects located in emerging markets, global capital can be more easily accessed with this approach. Sustainable practices can also be scaled upward.
Commercial Value for Businesses
For enterprises, net-zero tokenization unlocks definitive commercial gains not just sustainability. The most important of the benefits are right here.
Enhanced Transparency and Trust
Credibility does pose a major challenge when reporting about ESG. That climate finance achieves real impact is increasingly demanded for verifiable proof by investors and regulators. Immutable blockchain records each transaction plus every environmental outcome when tokenization happens. This strengthens trust among stakeholders, partners, and customers, makes audits smoother, and lowers the risk of greenwashing.
Improved Liquidity and Market Access
Customary green bonds or carbon credits often trap capital across years. This resulted in limited flexibility. Tokenized assets shift the game using markets that are tradable and liquid always. Businesses are able to raise funds faster also investors can exit earlier. Projects gain steady capital flows now free from bottlenecks. This liquidity also draws a wider investor base, including institutions as well as community-level participants.
Inclusive Investment Opportunities
Tokenization can let more people enter with some ease. For tokens, instead of requiring millions just to invest within a renewable energy project, they allow smaller contributions while still maintaining exposure for high-value assets. Imagine that a solar grid in Africa is funded by not just only large banks but also by small investors from worldwide locations, and each of those investors holds a stake by way of tokens. Businesses gather more capital since backers diversify by this inclusivity.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Smart contracts automate much of the administrative burden within customary climate finance since they handle compliance checks, reporting, and settlement. Transaction costs can be cut deeply while errors are lowered. Businesses save money then also speed up processes because they improve overall efficiency in managing ESG investments.
Streamlined ESG Reporting
Businesses that are operating globally must now comply with frameworks such as ISSB and TCFD. Tokenized assets merge into real-time reporting dashboards as green bond impacts, renewable energy generation, or carbon credit usage update automatically. This removes the headache of manually collecting data as well as it ensures organizations are ready for audits during the year.
Global Scalability
Scalability may be among the most compelling commercial values. Regions as well as asset classes can be replicated with established tokenization frameworks when they exist. Because of the fact that a renewable project in Latin America can follow along with the same tokenized model as one located in Europe, businesses are able to get global reach with minimal adaptation. Net-zero tokenization is scalable so it can grow into the long term. Tokenization has to be a strategy for long-term growth and it cannot just be an effort that is for one-off sustainability.
Ready to Scale your ESG Investments With Tokenized Assets?
Traditional vs. Tokenized Climate Finance
Projects regarding sustainability have been funded in part through customary climate finance tools. Green bonds, loans, and also carbon credits have played a role in that funding. Yet their shortcomings are clear when set beside tokenized models. Tokenizing delivers speed, transparency, and scalability that customary systems battle against to match.
Here’s how the two approaches compare:
Accessibility
In Traditional Finance, participation is often restricted just to large institutions and also to high-net-worth investors, so smaller contributors are locked out.
For tokenized finance, individual investors and even corporations can participate because of fractional ownership that is letting anyone access climate-positive project sizes that are smaller.
Liquidity
Green bonds and loans can typically lock up capital for a number of years. Due to this, Traditional Finance has rigid structures exhibiting little flexibility.
Tokenized Finance: Tokens can be traded 24/7 within secondary markets, and this allows investors to enter or exit positions more freely. Tokens allow investors to enter or exit positions with greater freedom.
Transparency
The reporting from Traditional Finance is quite fragmented also delayed along with being vulnerable to inconsistencies. Those problems obscure a real effect, actually.
In Tokenized Finance, blockchain records each and every transaction in real time, and that ensures traceability and lowers all of the risk that actors greenwash.
Efficiency
Traditional banking depends greatly on mediators. These dependencies escalate expenses and decelerate procedures.
Smart contracts reduce errors plus cut costs in Tokenized Finance because they automate compliance, settlement, and reporting.
Global Reach
Traditional Finance: Cross-border transactions face regulatory alongside operational hurdles, which limit scalability.
Digital tokens have the ability to be traded on a global scale without geographic restrictions. This enables faster capital mobilization throughout markets because they are traded without those restrictions.
Part 3
Implementation Challenges & Best Practices
While net-zero tokens unlock massive opportunities, they come with challenges. Businesses that explore this path must prepare for what concerns over scalability might cause, for what regulatory complexity entails, and for what issues data integrity brings. These hurdles, with the right frameworks and practices, are manageable. The good news is that they can turn into strengths.
Scalability and Blockchain Performance
Challenge: Public blockchains often face congestion as this leads to high transaction fees and slower speeds. This may be a bottleneck in climate finance projects that can be large-scale. These projects may be delayed.
Businesses should look into the Layer-2 solutions as more of a best practice. Models of hybrid design which join permissioned blockchains and public ones are viable options too. It guarantees extensibility and openly prevents compromises.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
For ESG reporting, carbon credits, and digital assets, varying rules exist in different regions. Navigating this patchwork is how one might describe overwhelming.
To align tokenization platforms to frameworks such as ISSB, TCFD, and EU ETS while one is tracking regulators such as MAS from Singapore or ADGM from UAE is Best Practice. The path can be smoothed by partnering with blockchain firms that are focused on compliance.
Data Integrity and Verification
Even tokenized assets without reliable data can lose credibility. Off-chain data for verification purposes must be trusted by users. Rates for carbon capture or output from renewable sources are examples.
Use IoT devices, trusted oracles, and zero-knowledge proofs: Ideal way for verification of privacy-preserving. Investors can trust the data without exposure of sensitive details.
Investor Education and Market Adoption
Tokenized assets are still unfamiliar for many investors and enterprises. That unfamiliarity makes adoption slower than the technology permits.
Businesses should include onboarding tools, coupled with education, in their platforms as a best practice. They build confidence and accelerate participation because they simplify interfaces, they report transparently, and they offer clear dashboards.
Cybersecurity and Risk Management
Just as with any solution that is blockchain-based, tokenization platforms present a challenge still. Tokenization platforms can be targeted by cyberattacks.
For ensuring security and for long-term trust, one needs regular audits as well as multi-signature wallets and also strong governance models.
In the event enterprises address all of these different challenges with proactive actions, they can certainly build tokenization models that all sustain and endure commercially.
Future Outlook for Net-Zero Tokenization
Tokenization will certainly direct the digital climate finance future. Analysts predict the tokenized real-world asset market might reach almost $19 trillion by 2033 with green, ESG-focused assets fueling growth’s important portion. Businesses that adopt tokenization on an early schedule will gain a competitive edge when demand rises for transparency, speed, and global accessibility.
As we look on ahead, we will see a deeper integration of AI-driven forecasting tools that can predict emission patterns, IoT-enabled precision tracking for renewable energy output and for carbon sequestration, and cross-chain interoperability that allows tokenized assets the ability to move smoothly across global markets. Regulators in key regions are warming up to tokenized ESG instruments also this sets the stage for mainstream adoption.
For many enterprises, this is not just an innovation that is to watch, it is an opportunity for them to take some action. Tokenization channels capital into climate projects as the standard infrastructure soon as well, and those moving now will position themselves as leaders in the trillion-dollar green economy.
Conclusion
Tokenization for net-zero changes technology giving transparency, liquidity, and true trust. It also can provide for a viable commercial path that then scales global climate finance. By converting real-world assets into tokenized instruments businesses can unlock new capital streams and engage a broader base of investors worldwide. In this way, they also can confidently meet with ESG goals. For enterprises ready to leap, Blockchain App Factory offers net-zero tokenization development services to empower enterprises as platforms arise. These platforms are compliant as well as future-proof therefore they are designed so as to fuel sustainability plus profitability.